Insights-Planning Archives
Capital Improvement Planning Helps Londonderry Township Improve Bridge Conditions At Lower Cost
/in Insights-Municipal, Insights-Planning, Insights-Transportation /by Judy Lincoln
We regularly hear about the condition of infrastructure in the United States, and many times the news is bad. Too often we hear about underground pipes breaking, roads crumbling, and bridges that need to be closed. Fortunately, in Londonderry Township, bridge conditions are actually pretty good.
Londonderry Township is specifically responsible for 13 bridges, all of which cross waterways and are less than 20’ in length. Closing any one of these bridges for safety concerns could cause a significant disruption to emergency access and general traffic flow. To avoid this, Londonderry Township asked HRG to assess all 13 structures and prioritize their maintenance and replacement needs. Our evaluation indicated that all 13 bridges were likely more than 50 years old, and six of them should be replaced within the next 3 – 10 years.
HRG worked with the township to create an approach to address this pressing infrastructure need without overburdening the township’s annual budget. The initial concept was to replace one bridge every other year for the six most critical structures. This would allow us to address the township’s most urgent needs without being forced into an emergency situation. It would also allow us to identify alternative funding for each bridge replacement and carefully plan any necessary road closures to minimize traffic interruption.
Londonderry’s program is a perfect example of infrastructure asset management and capital improvement planning. HRG has written extensively about the benefits of asset management and capital improvement planning. Essentially, a proactive approach to identifying infrastructure needs, prioritizing those needs, and planning for the necessary funding produces better infrastructure at a lower lifetime cost.
Thanks to this forward-looking approach, Londonderry Township is about to replace the last of the original six critical structures: a bridge on Swatara Creek Road. This project is funded through the partial use of a Dauphin County Local Share Gaming Grant.
Three bridges were replaced in 2016: one each on Beagle, Braeburn, and Hollendale Roads. The township bundled these bridges into one project and used extremely favorable funding from the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank. The first two bridges were replaced in 2012. Only one – on Round Top Road, was planned, but a second bridge on Foxianna Road required replacement after flooding from Tropical Storm Lee undermined the bridge. Fortunately, because of the emergency nature of the bridge replacement, the township was able to use federal disaster relief funding.
With the replacement of the six most critical bridge structures complete, the township will be able to focus on regular maintenance of the remaining seven structures to extend their useful life as long as possible. A proactive approach to maintenance like this means better driving conditions for township drivers over a longer period of time. The bridges will last longer, and the need for replacement will be delayed. This will save the township hundreds of thousands of dollars over time. (See an illustration of how this works with actual budget dollars in our article Better Roads for Less Money with Asset Management.)
The upkeep of bridges can seem like a daunting and expensive task, but it’s actually fairly simple if communities take a proactive approach. Consistent inspections to identify deterioration, regular maintenance to avoid worsening problems, and advanced planning for eventual replacement all combine to simplify bridge upkeep and ensure it remains affordable.
When it does come time for Londonderry Township to replace one of its structures, they will use the same judicial approach to ensure the infrastructure needs of the township are met in an economical manner.
(A version of this article originally appeared in the Londonderry Township newsletter.)
 Andrew Kenworthy, P.E., is the eastern region vice president of HRG. He has more than 25 years of experience in municipal engineering and land development/site design.
Andrew Kenworthy, P.E., is the eastern region vice president of HRG. He has more than 25 years of experience in municipal engineering and land development/site design.
How Dauphin County Has Turned a Small Surplus Into Major Infrastructure Improvements
/in Insights-Financial, Insights-Local Government, Insights-Planning, Insights-Transportation /by Judy LincolnThis article about the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank is excerpted from the February 2018 issue of Pennsylvania County News magazine. It is provided courtesy of the County Commissioners Association of Pennsylvania (CCAP) and is reprinted here with their permission. This is in no way an endorsement by CCAP of the products or services offered by HRG.
What would you do with an extra $350,000 per year in your county Liquid Fuels budget?
It sounds like a nice problem to have, doesn’t it?
That’s exactly the challenge Dauphin County faced six years ago as its aggressive bridge management program reached a very important milestone: The last load-posted, structurally deficient bridge in the county’s inventory was fully programmed to be replaced.
This video tells the story of the last structurally deficient bridge in Dauphin County. Once the county funded the replacement of this bridge, it had a surplus of Liquid Fuels money in its budget. They decided to use this surplus as seed money for an infrastructure bank that has funded more than a dozen roadway, traffic and bridge improvements throughout the county in just a few years. (Learn more about the county’s last structurally deficient bridge in this profile.)
For almost 30 years, the county had patiently and strategically planned the rehabilitation or replacement of 51 bridges. Close to 1/3 of its county-wide inventory had been structurally deficient at the time they embarked on this effort in 1984.
Now that hard work and determination was about to pay off. The county could drastically reduce its spending on bridge capital improvements by shifting from a replacement phase to a maintenance phase.
The county’s engineer, Herbert, Rowland & Grubic, Inc. (HRG), analyzed what investments would be necessary to proactively maintain the bridges and determined that the county would have an annual surplus of approximately $350,000 in Liquid Fuels funding beyond what was needed for maintenance expenses.
County commissioner Jeff Haste wanted to make sure the money was used wisely: “The county’s bridge management program had delivered tremendous value to our residents, drastically improving the safety and efficiency of our transportation system for drivers. We wanted to use this money to deliver even more value.”

County Commissioners Haste, Pries and Hartwick wanted to maximize the benefit of these surplus dollars for county residents. The infrastructure bank approach has allowed them to fund more than $11 million in improvements with an initial investment of $1 million.
Haste and his fellow commissioners, Mike Pries and George P. Hartwick, III, were thinking big, but regulatory requirements threatened to make the impact of this money small.
“Because of the forced distribution procedure associated with Liquid Fuels funding,” Haste explained, “the county had to come up with a use for this money or disburse it evenly to all 40 of our member municipalities.”
On average, each municipality would’ve received less than $10,000, which is too small a sum to do anything more significant that buy a little extra road salt for the winter.
Yet, even if the county used the entire $350,000 surplus itself, they wouldn’t be able to cover the cost of even one small capital improvement like a single-span bridge replacement (which typically costs between $500,000 to $1 million).
Haste, Pries and Hartwick wanted to have a larger impact, so they asked county staff to collaborate on a solution with the engineer who’d designed the successful bridge management program in the first place.
Together, they came up with an innovative program in which the county would use this annual Liquid Fuels surplus to dramatically reduce the cost of infrastructure improvements for local municipalities.
How the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank Works
The Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank offers loans to municipalities (or private sector companies) to design and construct local roadway, bridge and traffic improvements – at unbeatably low interest rates. Municipalities can borrow money for as little as 0.5% interest. (Private sector borrowers pay a 1% interest rate.)
As an added bonus, Dauphin County provides loan recipients with optional engineering design support. This is very beneficial to smaller municipalities who have never completed a large capital improvement project before and may not know how to navigate the complicated state and federal requirements these projects must meet. An experienced consultant can save these municipalities from costly and time-consuming mistakes and re-work.
But, if $350,000 wasn’t enough money for the county to complete one major capital improvement project on its own, how can it use that money to fund multiple projects by its municipalities?
The power of partnerships.
Dauphin County multiplies the value of its $350,000 investment by combining it with additional funding from Pennsylvania’s state infrastructure bank.
Essentially, the county uses its Liquid Fuels surplus to make it more affordable for municipalities and private sector organizations to borrow money from the state by paying a portion of their interest. Interest on Pennsylvania Infrastructure Bank loans can vary, but it is currently 2.125% at the time this article is being written.
A municipality could borrow funds directly from the Pennsylvania Infrastructure Bank at an interest rate of just over 2%, or it could borrow from Dauphin County, and the county would pay approximately 75% of the interest expenses.
The following diagram shows exactly how the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank funds its projects:
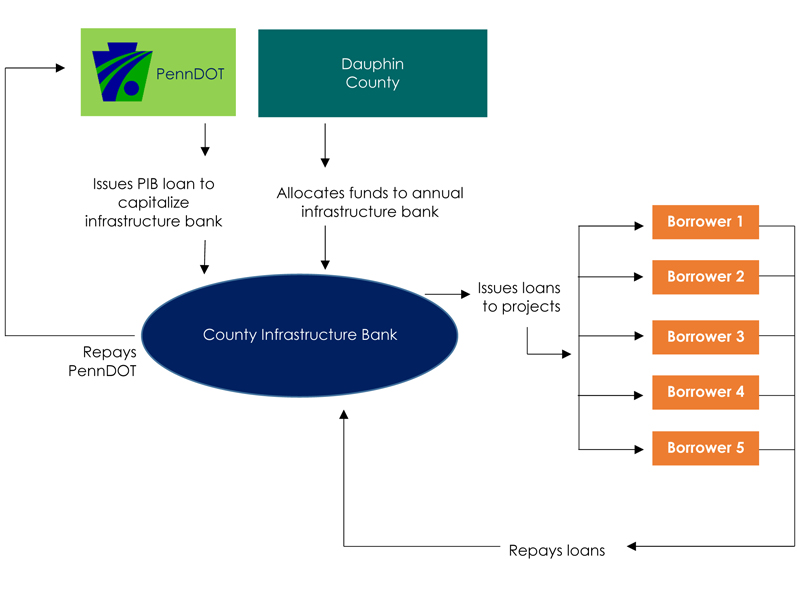
It is a self-renewing process. As municipalities or private sector organizations repay their loan to the county infrastructure bank, the county repays PennDOT. Once the debt is satisfied, the county has the ability to issue new loans to other municipalities or private sector companies.
For some municipalities, the cost savings provided by an infrastructure bank loan can be the difference between being able to move forward with a project at all or having to postpone it a few more years.
In the first three years of the infrastructure bank program, Dauphin County multiplied close to $1 million in Liquid Fuels funding into $11 million worth of improvements to the local transportation system: 7 bridges, one traffic signal, one streetscape, and one intersection improvement.
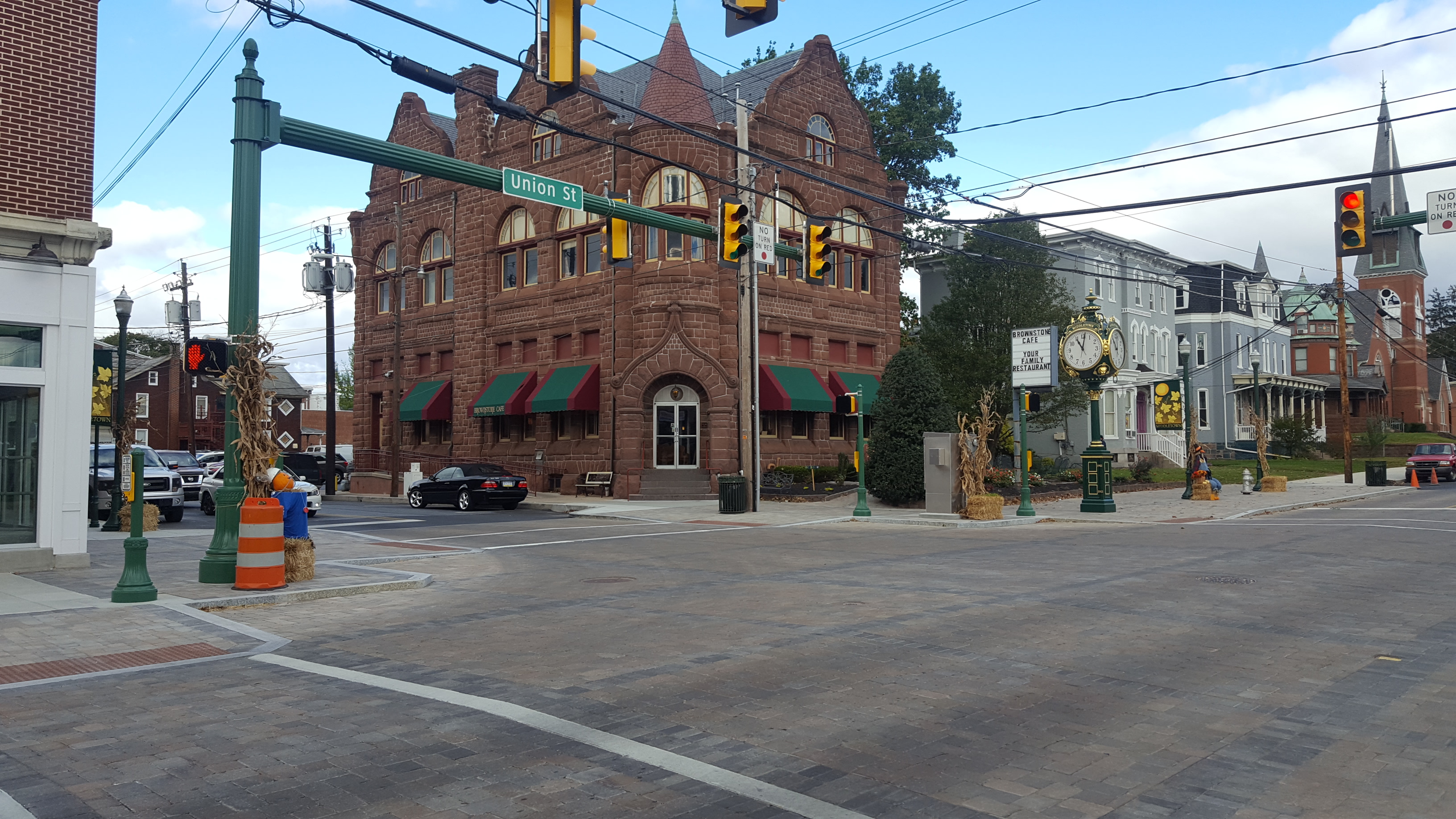

This streetscape project in Middletown Borough is one of the projects that has been funded by the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank. You can read more about the award-winning project and its potential economic benefit for the community in this article from The Authority.
“This is the kind of dramatic impact we were hoping to have,” says Pries, who oversees Dauphin County’s Community and Economic Development Department.
“The success of our bridge program and the creation of the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank has allowed us to help residents without the need to raise property taxes. Unlike many other parts of the country, our residents don’t have to worry about crumbling bridges and road networks.”
Read more about the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank, the benefits of implementing an infrastructure bank in your county, and other counties that are considering a program of their own in the February 2018 issue of Pennsylvania County News.

Brian Emberg, P.E., is senior vice president and chief technical officer of Herbert, Rowland & Grubic, Inc. (HRG). He helped design Dauphin County’s bridge management system and worked with the county to develop the Dauphin County Infrastructure Bank. He has more than 30 years of experience designing roadways and bridges and is particularly skilled in creating unique funding solutions to help local governments accomplish their infrastructure goals with limited revenue. You can contact Brian by phone at (717) 564-1121 or by email at bemberg@hrg-inc.com
Form-Based Zoning Can Bring Municipalities and Developers Together on the Walkable Communities Buyers Want
/in Insights-Land Development, Insights-Local Government, Insights-Municipal, Insights-Planning, Insights-Residential /by Judy LincolnPhoto by North Charleston. Published here under a Creative Commons license.
The National Association of Realtors (NAR) recently released the results of a nationwide poll showing millennials increasingly prefer walkable communities over the spread-out developments in many present-day suburbs. Other studies have confirmed similar preferences for walkable neighborhoods and mixed-use development; however, traditional zoning approaches, which emphasize low-density development and a separation of land uses, makes it difficult for residential developers to obtain approval for these communities. This article explores the rise in popularity of the walkable community and discusses how residential developers and municipal planners can use form-based zoning to create a community that meets the needs of everyone.
The Case for Walkable Communities
In 2013, NAR’s Community Preference Survey found that 60% of respondents preferred a neighborhood that mixes housing with stores and businesses within walking distance, and 55% would give up a home with a bigger yard in order to get one within walking distance of schools, stores and restaurants.
Additionally, a study by Gary Pivo at the University of Arizona’s Urban Planning Program and Jeffrey Fisher at Indiana University’s Kelly School of Business found that – other factors being equal – enhanced walkability increased the value of both residential and commercial properties. Using data from the National Council of Real Estate Investment Fiduciaries and Walk Score, they compared more than 4,000 office, apartment, retail and industrial properties and determined that a 10% increase in walkability increased property value by up to 9% for all but the industrial properties. (There was no discernible impact on industrial properties with a higher walkability score.)
This is in line with other studies of traditional neighborhood developments (TND) published in Real Estate Economics and the Journal of Urban Economics, which found that buyers were willing to pay between 12-15% more for pedestrian-friendly homes in the studied neighborhoods, compared to similar homes in neighboring low-density communities.
Increased property values benefit the developer selling the home, but they also benefit the local municipality as they increase property tax revenues. In addition, high density, walkable communities reduce the amount of infrastructure (such as roadways, traffic signals, water and sewer line extensions) needed to connect spread-out developments, which can save the municipality money that would’ve been needed to maintain that infrastructure.
The most important reason for municipalities to consider making their zoning friendlier to walkable communities, however, might be their desire to stay competitive as a place people want to live.
Millennials represent a demographic of 80 million people, and they are the generation that will be buying homes and putting down roots in the years to come. Michael Myers, a managing director at The Rockefeller Foundation, is quoted in an article on The Atlantic’s CityLab website, saying, “As we move from a car-centric model of mobility to a nation that embraces more sustainable transportation options, millennials are leading the way…Cities that don’t invest in [these options] stand to lose out in the long run.”
Bridging the Municipal-Developer Gap with Form-Based Zoning
If municipalities and developers agree that walkable communities can be beneficial, why aren’t more of them being built?
Over the past few years, these communities have become more and more popular with both developers and municipalities, but acceptance still is not widespread. Traditional zoning ordinances could be one of the reasons why.
Traditional zoning ordinances separate land uses into distinct zones: Commercial is separate from residential. Single family homes are separate from apartments and townhomes, etc. This prevents the construction of developments that combine commercial and residential uses of different types in one space like modern walkable communities do. In addition, traditional zoning has emphasized a low-density approach because communities associate higher density with a loss of open space and community character and fear higher density developments will drain community resources. However, developers require a higher density approach in order to make the many amenities (such as recreational facilities and civic and commercial spaces) affordable in a typical walkable community plan.
But form-based zoning could be the bridge that closes the gap between a community’s concerns and a developer’s needs.
Rather than fixating on density values and strict land use definitions, municipalities using a form-based zoning approach create a vision for the type of community they’d like to have and set standards to realize that vision. If they want a community that encourages walking and social interaction in public spaces, they can set standards that will promote these activities. For example, Public Space standards can specify the types of pedestrian amenities, greenspaces and recreation requirements that make a place feel safe, comfortable and walkable. They can also set the size of a standard block and govern how roadways and pedestrian amenities interconnect. (Keeping the size of blocks small will make them more manageable for walkers, and interconnecting streets will provide shorter routes and more evenly distribute car traffic throughout the roadway network. This will, in turn, have the added benefit of reducing congestion that comes from concentrating cars on just a few heavily travelled corridors, as is common in many traditionally zoned communities today.)
By using a form-based approach, municipalities can focus more on the form and feel of a community, instead of limiting development to strictly separated zones with a one-size-fits-all regulation of lot sizes.
In turn, residents enjoy the quality of life they seek, and municipalities can continue to attract growth, maintain a healthy tax base, and reduce the expenses associated with sprawling infrastructure. Meanwhile developers are able to meet a market demand profitably without navigating an unnecessarily lengthy entitlements process.
This type of approach allows communities to remain relevant and competitive in the decades to come as millennials age, take their resources and preferences to market, have kids and nurture the next generation. Municipalities and developers that dismiss these trends as merely a fad may be taking a big risk. Is it worth it? We will know in 20 years.
HRG excels at bringing developers and municipalities together to meet the needs of a community in a way that benefits all parties. To discuss how walkable communities could benefit you, please contact us.
